In Quart de Poblet, Spain, the QCATI team is advancing into the second phase of its work under the CLIMAAX framework, refining Climate Risk Assessments (CRAs) through the integration of local datasets and updated climate projections.
Recent efforts have focused on heatwave workflows, using high-resolution data from the Spanish Meteorological Agency (AEMET) and incorporating demographic information on the elderly population (65+) to map urban heat island vulnerabilities by census tract. An upcoming participatory session with senior citizens will share these findings and raise local awareness about heat risks and adaptation options.
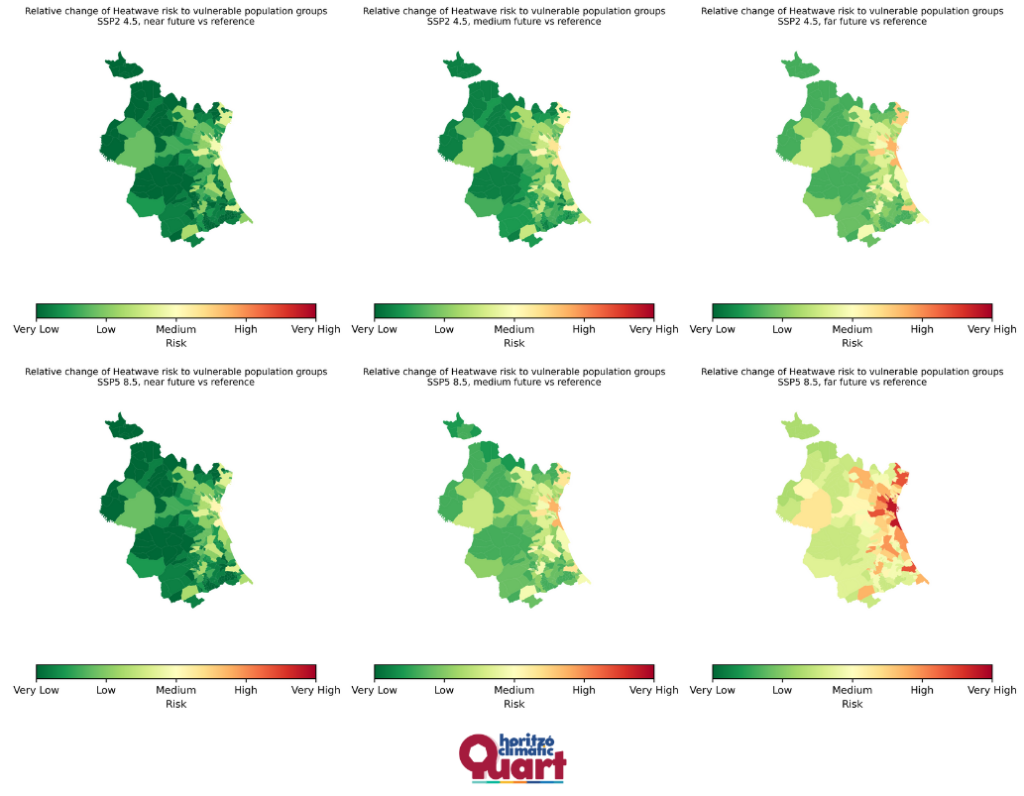
At the same time, the team is enhancing the river flood risk analysis using new flood maps from the Júcar River Basin Authority (CHJ) and updated regional land use data. The comparison between modeled flood events—such as the T=500 return period scenario—and the observed October 2024 flood provides valuable insight into local hydrological dynamics and climate trends affecting the area.
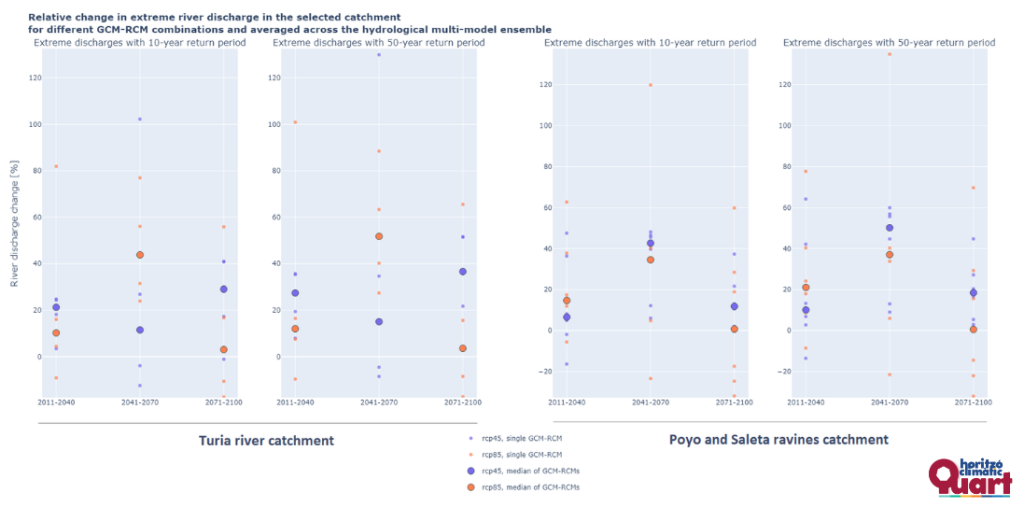
Looking ahead, the project aims to expand community participation, engaging local environmental, agricultural, and sustainability associations to strengthen climate resilience and promote collective action toward a more sustainable future for Quart de Poblet.
